⏳ 序言
前面的文章中讲解了各种数据结构,那么今天,顺着数据结构与算法这个话题,我们来谈谈算法。算法一般分为两种,一种是排序算法,另一种是搜索算法。
在今天的文章中,将概括排序和搜索在 js 中的应用,同时讲解常见的 5 种排序算法,分别是:冒泡排序、选择排序、插入排序、归并排序和快速排序。以及常见的两种搜索算法:顺序搜索和二分搜索。
一起来学习吧~🧐
🧭 一、文章结构抢先知
在文章开讲之前,我们先用一张思维导图,来辅助大家了解文章结构。详情见下图 👇
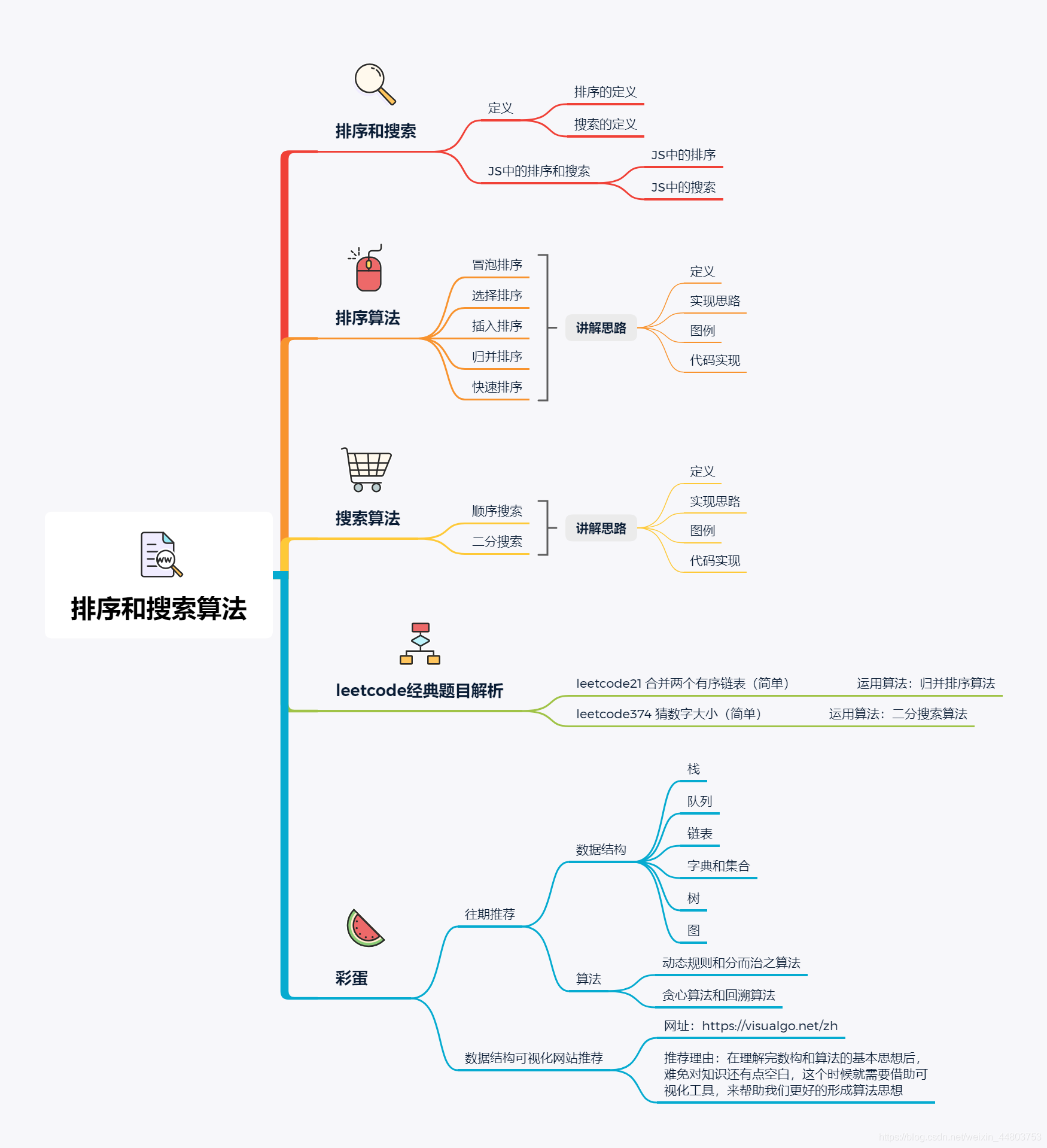
了解完思维导图后,接下来开始进入本文的讲解~
⌚ 二、排序和搜索
1、定义
- 排序: 所谓排序,就是把某个乱序的数组变为升序或降序的数组。
- 搜索: 所谓搜索,就是找出数组中某个元素的下标。
2、JS 中的排序和搜索
JS中的排序:数组的sort()方法。JS中的搜索:数组中的indexOf()方法。
⏰ 三、排序算法
1、冒泡排序 💡
(1)定义
冒泡排序,即比较相邻的两个元素。如果第一个比第二个大,就左右交换它们两个,依次进行 n 轮。
(2)实现思路
- 比较所有相邻元素,如果第一个比第二个大,则交换它们。
- 一轮下来,可以保证最后一个数是最大的。
- 执行 n - 1 轮,就可以完成排序。
(3)图例
下面用一个视频来演示冒泡排序的全过程。详情见下图 👇
video:https://live.csdn.net/v/embed/172647
(4)代码实现
/**
* @description 冒泡排序
*/
Array.prototype.bubbleSort = function () {
for (let i = 0; i < this.length - 1; i++) {
for (let j = 0; j < this.length - 1 - i; j++) {
if (this[j] > this[j + 1]) {
const temp = this[j];
this[j] = this[j + 1];
this[j + 1] = temp;
}
}
}
};
const arr = [5, 4, 3, 2, 1];
arr.bubbleSort();
console.log(arr); //[1, 2, 3, 4, 5]/**
* @description 冒泡排序
*/
Array.prototype.bubbleSort = function () {
for (let i = 0; i < this.length - 1; i++) {
for (let j = 0; j < this.length - 1 - i; j++) {
if (this[j] > this[j + 1]) {
const temp = this[j];
this[j] = this[j + 1];
this[j + 1] = temp;
}
}
}
};
const arr = [5, 4, 3, 2, 1];
arr.bubbleSort();
console.log(arr); //[1, 2, 3, 4, 5]2、选择排序 💡
(1)定义
选择排序,即在要排序的一组数中,选出最小的数与第一个位置的数交换;然后再剩下的数当中再找最小的数与第二个位置的数交换,如此循环到倒数第二个数和最后一个数比较为止。
(2)实现思路
- 找到数组中的最小值,选中它并将其放在第一位。
- 接着找到第二小的值,选中它并将其放置在第二位。
- 以此类推,执行 n - 1 轮。
(3)图例
下面用一个视频来演示选择排序的全过程。详情见下图 👇
video:https://live.csdn.net/v/embed/172650
(4)代码实现
/**
* @description 选择排序
*/
Array.prototype.selectSort = function () {
for (let i = 0; i < this.length - 1; i++) {
let indexMin = i;
for (let j = i; j < this.length; j++) {
if (this[j] < this[indexMin]) {
indexMin = j;
}
}
if (indexMin !== i) {
const temp = this[i];
this[i] = this[indexMin];
this[indexMin] = temp;
}
}
};
const arr = [5, 4, 3, 2, 1];
arr.selectSort();
console.log(arr); //[1, 2, 3, 4, 5]/**
* @description 选择排序
*/
Array.prototype.selectSort = function () {
for (let i = 0; i < this.length - 1; i++) {
let indexMin = i;
for (let j = i; j < this.length; j++) {
if (this[j] < this[indexMin]) {
indexMin = j;
}
}
if (indexMin !== i) {
const temp = this[i];
this[i] = this[indexMin];
this[indexMin] = temp;
}
}
};
const arr = [5, 4, 3, 2, 1];
arr.selectSort();
console.log(arr); //[1, 2, 3, 4, 5]3、插入排序 💡
(1)定义
插入排序是一种将指定元素与某个有序区域比较并交换位置的排序算法。
(2)实现思路
- 从第二个数开始往前比。
- 比它大就往后排。
- 以此类推进行到最后一个数。
(3)图例
下面用一个视频来演示插入排序的全过程。详情见下图 👇
video: https://live.csdn.net/v/embed/172652
(4)代码实现
/**
* @description 插入排序
*/
Array.prototype.insertionSort = function () {
for (let i = 1; i < this.length; i++) {
const temp = this[i];
let j = i;
while (j > 0) {
if (this[j - 1] > temp) {
this[j] = this[j - 1];
} else {
break;
}
j -= 1;
}
this[j] = temp;
}
};
const arr = [6, 2, 3, 4, 5];
arr.insertionSort();
console.log(arr); // [2, 3, 4, 5, 6]/**
* @description 插入排序
*/
Array.prototype.insertionSort = function () {
for (let i = 1; i < this.length; i++) {
const temp = this[i];
let j = i;
while (j > 0) {
if (this[j - 1] > temp) {
this[j] = this[j - 1];
} else {
break;
}
j -= 1;
}
this[j] = temp;
}
};
const arr = [6, 2, 3, 4, 5];
arr.insertionSort();
console.log(arr); // [2, 3, 4, 5, 6]4、归并排序 💡
(1)定义
归并排序的实现是使用了一种分而治之的思想,即将一个数组不断地通过两两分组的方式进行比较,最后知道所有元素都被分到一组里,达到整体有序的目的。
(2)实现思路
- 划分问题:把序列分成元素个数尽量相等的两半;
- 递归求解:把两半元素分别排序;
- 合并问题:把两个有序表合并成一个。
(3)图例
下面用一个视频来演示归并排序的全过程。详情见下图 👇
video: https://live.csdn.net/v/embed/172653
(4)代码实现
/**
* @description 归并排序
*/
Array.prototype.mergeSort = function () {
const rec = (arr) => {
if (arr.length === 1) {
return arr;
}
const mid = Math.floor(arr.length / 2);
const left = arr.slice(0, mid);
const right = arr.slice(mid, arr.length);
const orderLeft = rec(left);
const orderRight = rec(right);
const res = [];
while (orderLeft.length || orderRight.length) {
if (orderLeft.length && orderRight.length) {
res.push(
orderLeft[0] < orderRight[0] ? orderLeft.shift() : orderRight.shift()
);
} else if (orderLeft.length) {
res.push(orderLeft.shift());
} else if (orderRight.length) {
res.push(orderRight.shift());
}
}
return res;
};
const res = rec(this);
res.forEach((n, i) => {
this[i] = n;
});
return res;
};
const arr = [5, 4, 3, 2, 1];
// arr.mergeSort();
console.log(arr.mergeSort()); // [1, 2, 3, 4, 5]/**
* @description 归并排序
*/
Array.prototype.mergeSort = function () {
const rec = (arr) => {
if (arr.length === 1) {
return arr;
}
const mid = Math.floor(arr.length / 2);
const left = arr.slice(0, mid);
const right = arr.slice(mid, arr.length);
const orderLeft = rec(left);
const orderRight = rec(right);
const res = [];
while (orderLeft.length || orderRight.length) {
if (orderLeft.length && orderRight.length) {
res.push(
orderLeft[0] < orderRight[0] ? orderLeft.shift() : orderRight.shift()
);
} else if (orderLeft.length) {
res.push(orderLeft.shift());
} else if (orderRight.length) {
res.push(orderRight.shift());
}
}
return res;
};
const res = rec(this);
res.forEach((n, i) => {
this[i] = n;
});
return res;
};
const arr = [5, 4, 3, 2, 1];
// arr.mergeSort();
console.log(arr.mergeSort()); // [1, 2, 3, 4, 5]5、快速排序 💡
(1)定义
快速排序,即通过一趟排序,将需要排序的数据分割成独立的两部分,其中一部分的所有数据比另外一部分的所有数据都要小,然后再按此方法对这两部分数据分别进行快速排序,整个排序过程可以递归进行,以此达到整个数据变成有序序列。
(2)实现思路
- 分区:从数组中任意选择一个“基准”,所有比基准小的元素放在基准前面,比基准大的元素放在基准的后面。
- 递归:递归的对基准前后的子数组进行分区。
(3)图例
下面用一个视频来演示快速排序的全过程。详情见下图 👇
video: https://live.csdn.net/v/embed/171489
(4)代码实现
/**
* @description 快速排序
*/
/**
* 实现思路:
* 1.先选一个元素作为基点pivot;
* 2.将其余元素中所有比pivot小的值放在pivot的左边,将所有比pivot大的值放在pivot的右边;
* 3.然后分别对pivot左边的所有元素和右边的所有元素,从步骤1开始依次进行排序,直到所有元素完整有序。
*/
Array.prototype.quickSort = function () {
const rec = (arr) => {
if (arr.length === 1) {
return arr;
}
const left = [];
const right = [];
const mid = arr[0];
for (let i = 1; i < arr.length; i++) {
if (arr[i] < mid) {
left.push(arr[i]);
} else {
right.push(arr[i]);
}
}
return [...rec(left), mid, ...rec(right)];
};
const res = rec(this);
res.forEach((n, i) => {
this[i] = n;
});
return res;
};
const arr = [2, 4, 5, 3, 1];
console.log(arr.quickSort()); // [1, 2, 3, 4, 5]/**
* @description 快速排序
*/
/**
* 实现思路:
* 1.先选一个元素作为基点pivot;
* 2.将其余元素中所有比pivot小的值放在pivot的左边,将所有比pivot大的值放在pivot的右边;
* 3.然后分别对pivot左边的所有元素和右边的所有元素,从步骤1开始依次进行排序,直到所有元素完整有序。
*/
Array.prototype.quickSort = function () {
const rec = (arr) => {
if (arr.length === 1) {
return arr;
}
const left = [];
const right = [];
const mid = arr[0];
for (let i = 1; i < arr.length; i++) {
if (arr[i] < mid) {
left.push(arr[i]);
} else {
right.push(arr[i]);
}
}
return [...rec(left), mid, ...rec(right)];
};
const res = rec(this);
res.forEach((n, i) => {
this[i] = n;
});
return res;
};
const arr = [2, 4, 5, 3, 1];
console.log(arr.quickSort()); // [1, 2, 3, 4, 5]⏲️ 四、搜索算法
1、顺序搜索 💡
(1)定义
顺序搜索是指将每一个数据结构中的元素和我们要找的元素做比较。顺序搜索是最低效的一种搜索算法。
(2)实现思路
- 遍历数组。
- 找到跟目标值相等的元素,就返回它的下标。
- 遍历结束后,如果没有搜索到目标值,就返回-1。
(3)代码实现
/**
* @description 顺序搜素
*/
Array.prototype.sequentialSearch = function (item) {
for (let i = 0; i < this.length; i++) {
if (this[i] === item) {
return i;
}
}
return -1;
};
const res = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5].sequentialSearch(3);
console.log(res); // 2/**
* @description 顺序搜素
*/
Array.prototype.sequentialSearch = function (item) {
for (let i = 0; i < this.length; i++) {
if (this[i] === item) {
return i;
}
}
return -1;
};
const res = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5].sequentialSearch(3);
console.log(res); // 22、二分搜索 💡
(1)定义
二分搜索,也称折半搜索,它是一种效率较高的搜索方法。但是,折半搜索要求线性表必须采用顺序存储结构,而且表中元素按关键字有序排列。
(2)实现思路
- 从数组的中间元素开始,如果中间元素正好是目标值,则搜索结束。
- 如果目标值大于或小于中间元素,则在大于或小于中间元素的那一半数组中搜索。
(3)代码实现
/**
* @description 二分搜索
*/
Array.prototype.binarySearch = function (item) {
let low = 0;
let high = this.length - 1;
while (low <= high) {
const mid = Math.floor((low + high) / 2);
const element = this[mid];
if (element < item) {
low = mid + 1;
} else if (element > item) {
high = mid - 1;
} else {
return mid;
}
}
return -1;
};
const res = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5].binarySearch(1);
console.log(res); // 0/**
* @description 二分搜索
*/
Array.prototype.binarySearch = function (item) {
let low = 0;
let high = this.length - 1;
while (low <= high) {
const mid = Math.floor((low + high) / 2);
const element = this[mid];
if (element < item) {
low = mid + 1;
} else if (element > item) {
high = mid - 1;
} else {
return mid;
}
}
return -1;
};
const res = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5].binarySearch(1);
console.log(res); // 0⏱️ 五、leetcode 经典题目解析
1、leetcode21 合并两个有序链表(简单)
(1)题意
附上题目链接:leetcode21 合并两个有序链表
将两个升序链表合并为一个新的 升序 链表并返回。新链表是通过拼接给定的两个链表的所有节点组成的。
输入输出示例:
- 输入:
l1= [1,2,4],l2= [1,3,4] - 输出: [1,1,2,3,4,4]
(2)解题思路
- 与归并排序中的合并两个有序数组相似。
- 将数组替换成链表就能解决此 题。
(3)解题步骤
- 新建一个新链表,作为返回结果。
- 用指针遍历两个有序链表,并比较两个链表的当前节点,较小者先接入新链表,并将指针后移一步。
- 链表遍历结束,返回新链表。
(4)代码实现
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* function ListNode(val, next) {
* this.val = (val===undefined ? 0 : val)
* this.next = (next===undefined ? null : next)
* }
*/
/**
* @param {ListNode} l1
* @param {ListNode} l2
* @return {ListNode}
*/
var mergeTwoLists = function (l1, l2) {
const res = new ListNode(0);
let p = res;
let p1 = l1;
let p2 = l2;
while (p1 && p2) {
if (p1.val < p2.val) {
p.next = p1;
p1 = p1.next;
} else {
p.next = p2;
p2 = p2.next;
}
p = p.next;
}
if (p1) {
p.next = p1;
}
if (p2) {
p.next = p2;
}
return res.next;
};/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* function ListNode(val, next) {
* this.val = (val===undefined ? 0 : val)
* this.next = (next===undefined ? null : next)
* }
*/
/**
* @param {ListNode} l1
* @param {ListNode} l2
* @return {ListNode}
*/
var mergeTwoLists = function (l1, l2) {
const res = new ListNode(0);
let p = res;
let p1 = l1;
let p2 = l2;
while (p1 && p2) {
if (p1.val < p2.val) {
p.next = p1;
p1 = p1.next;
} else {
p.next = p2;
p2 = p2.next;
}
p = p.next;
}
if (p1) {
p.next = p1;
}
if (p2) {
p.next = p2;
}
return res.next;
};2、leetcode374 猜数字大小(简单)
(1)题意
猜数字游戏的规则如下:
每轮游戏,我都会从 1 到 n 随机选择一个数字。 请你猜选出的是哪个数字。
如果你猜错了,我会告诉你,你猜测的数字比我选出的数字是大了还是小了。
你可以通过调用一个预先定义好的接口 int guess(int num) 来获取猜测结果,返回值一共有 3 种可能的情况(-1,1 或 0):
-1:我选出的数字比你猜的数字小 pick < num
1:我选出的数字比你猜的数字大 pick > num
0:我选出的数字和你猜的数字一样。恭喜!你猜对了!pick == num
返回我选出的数字。
输入输出示例:
- 输入: n = 10, pick = 6
- 输出: 6
(2)解题思路
- 二分搜索。
- 调用 guess 函数,来判断中间元素是否是目标值。
(3)解题步骤
- 从数组的中间元素开始,如果中间元素正好是目标值,则搜索过程结束。
- 如果目标值大于或者小于中间元素,则在数组大于或小于中间元素的那一半中查找。
(4)代码实现
/**
* Forward declaration of guess API.
* @param {number} num your guess
* @return -1 if num is lower than the guess number
* 1 if num is higher than the guess number
* otherwise return 0
* var guess = function(num) {}
*/
/**
* @param {number} n
* @return {number}
*/
var guessNumber = function (n) {
let low = 1;
let high = n;
while (low <= high) {
const mid = Math.floor((low + high) / 2);
const res = guess(mid);
if (res === 0) {
return mid;
} else if (res === 1) {
low = mid + 1;
} else if (res === -1) {
high = mid - 1;
}
}
};/**
* Forward declaration of guess API.
* @param {number} num your guess
* @return -1 if num is lower than the guess number
* 1 if num is higher than the guess number
* otherwise return 0
* var guess = function(num) {}
*/
/**
* @param {number} n
* @return {number}
*/
var guessNumber = function (n) {
let low = 1;
let high = n;
while (low <= high) {
const mid = Math.floor((low + high) / 2);
const res = guess(mid);
if (res === 0) {
return mid;
} else if (res === 1) {
low = mid + 1;
} else if (res === -1) {
high = mid - 1;
}
}
};🕙 六、结束语
算法在前端中的应用还是蛮广泛的,比如 js 中的 sort() 和 indexOf() 是基于排序和搜索算法来实现的。同时,算法在也是前端面试中的一大必考点,对于不会算法的开发者来说,无形之中与别人的核心竞争力就会被削减了一大半。
本文主要讲解了一些常见的排序和搜索的基础实现,后续大家还可以继续深挖一些其他场景,举一反三,慢慢的理解就会越来越深入了~
到这里,排序和搜索算法的讲解就结束啦!希望对大家有帮助~
🐣 彩蛋 One More Thing
🏷️ 往期推荐
队列 👉详解队列在前端的应用,深剖 JS 中的事件循环 Eventloop,再了解微任务和宏任务
字典和集合 👉ES6 的 Set 和 Map 你都知道吗?一文了解集合和字典在前端中的应用
图 👉太平洋大西洋水流问题如何解决?一文了解图在前端中的应用
动态规则和分而治之算法 👉一文了解分而治之和动态规则算法在前端中的应用
贪心算法和回溯算法 👉一文了解贪心算法和回溯算法在前端中的应用
🏷️ 网站推荐
文章重的可视化动图用到的是 visualgo 网站进行录屏,该网站几乎涵盖了所有数据结构和算法的实现,包括但不限于排序、位掩码、哈希表、二叉堆和循环查找等等动图的功能。戳此链接可直接进入网站体验可视化~
